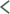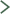TRIGGER FINGER AND TRIGGER THUMB
Introduction
Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the
movement of the tendons as they bend the fingers or thumb toward
the palm of the hand. This movement is called flexion.
Causes of Trigger Finger or Thumb
Triggering is usually the result of a thickening in the tendon that
forms a nodule, or knob. The pulley ligament may thicken as well.
The constant irritation from the tendon repeatedly sliding through
the pulley causes the tendon to swell in this area and create the
nodule. Rheumatoid arthritis, partial tendon lacerations, repeated
trauma from pistol- gripped power tools, or long hours grasping a
steering wheel can cause triggering. Infection or damage to the
synovium causes a rounded swelling (nodule) to form in the tendon.
Triggering can also be caused by a congenital defect that forms a
nodule in the tendon. The condition is not usually noticeable until
infants begin to use their hands.
Symptoms of Trigger Finger or Thumb
- Pain and a funny clicking sensation when the finger or thumb is bent.
- Tenderness usually occurs over the area of the nodule, at the
bottom of the finger or thumb.